Press Release: It is becoming increasingly clear that the energy transition is something that can no longer be disputed in Europe. It is required in a variety of ways by governments in and outside the EU, and it affects essentially all sectors of the economy. The key to decarbonisation in most European countries will be renewable sources, especially solar and wind power plants. And of course, this is a costly and lengthy process. Its importance is currently enhanced by the European Union's efforts to eliminate dependence on Russian fossil resources before the year 2030. These goals have been summarized in a new joint plan of European countries called REPowerUp Europe, which defines ways to get safer, more sustainable and more affordable energy and accelerate electrification overall. In this article, we will focus on solar energy, or photovoltaics, the problems of obtaining it and distribution to the network, and we will introduce some of the already implemented projects.
1. The coming years will see changes in the way we obtain and distribute electricity. What role will solar energy play in this regard?
The growth of electricity production from the sun is necessary in a situation where the demand for a cleaner and safer environment is increasing. Already today, solar energy in the Czech Republic is a significant source, which annually generates 3% of all electrical production, and the total potential is far from being used. A severalfold increase in the share of solar electricity in the Czech energy mix can be expected, which will also lead to raising the energy system to a new level with a transformation similar to that caused by the Internet in the dissemination of information. This change will require the need for new technical solutions for the joint balanced operation of multiple energy sources and storages to overlap and complement each other. Likewise, there will be a need to expand business cooperation between large and small suppliers and consumers in a situation where consumers will simultaneously become suppliers, or prosumers.
2. What photovoltaic projects are you working on at EEIC?
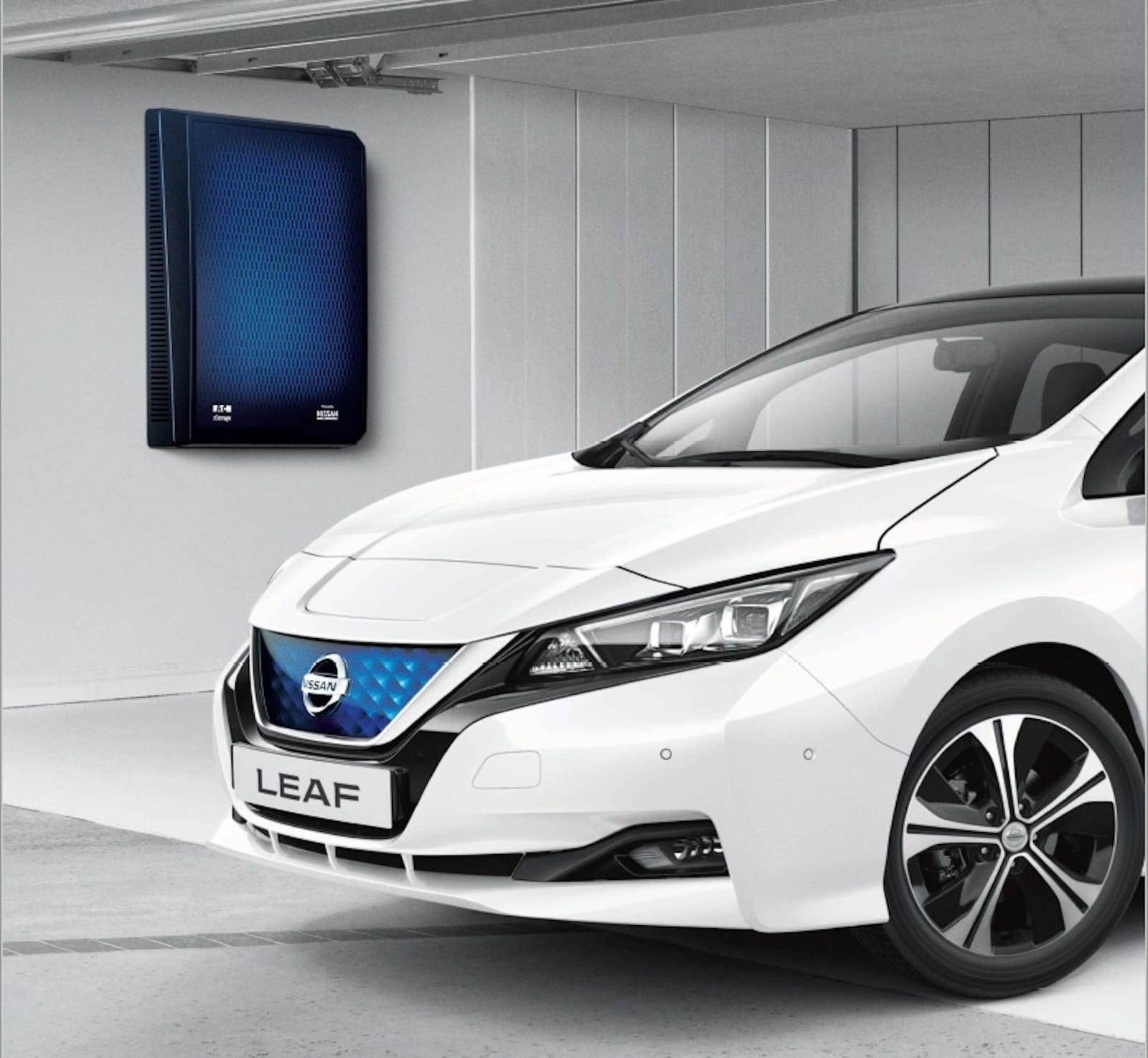
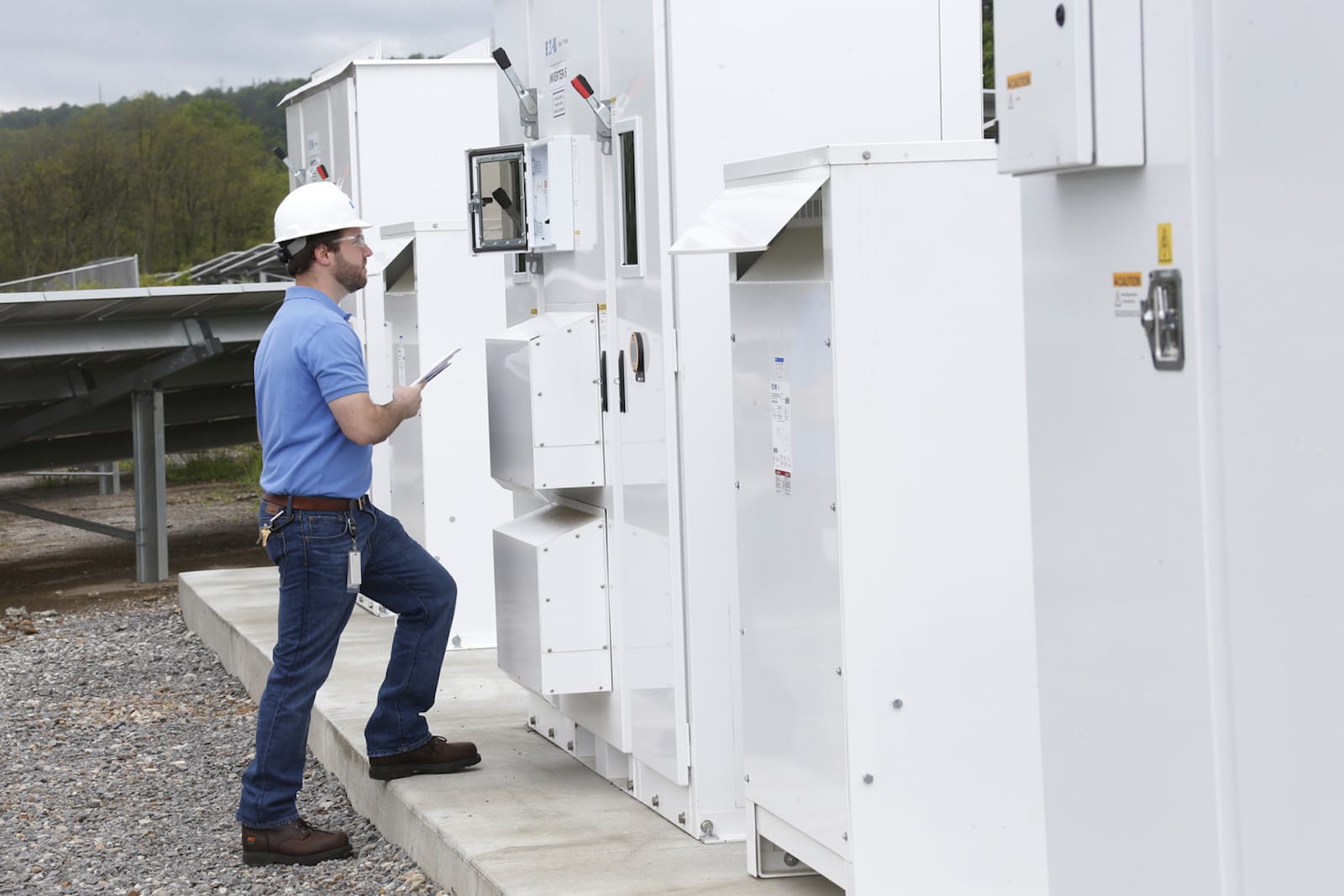
Eaton has a wide range of products for the distribution and handling of solar energy from classic switches, circuit breakers, fuses made especially for solar power plants, to battery storage of the xStorage series for storing solar energy. For example, in the EEIC innovation center in Roztoky near Prague, we are working on a new type of protection in the distribution line of solar power plants against an arc fault, which can arise from imperfect connection or damage to the cabling, and ultimately can lead to a fire. As part of a project to connect various Eaton products into one system, we are working with the xStorage Home unit. This device includes a battery pack and a hybrid inverter. xStorage Home offers you to store solar energy, renewable energy produced during the day for use morning, noon and night. Even in the event of a grid failure, the xStorage Home system provides energy to households, for example for lighting and security systems.

We are also working on microgrid control, which is an electrically system that can work together with the distribution network, but can disconnect and work independently for some time, for example in the event of a fault in the distribution system. We have installed a solar power plant with an output of up to 17 kWp and we plan to expand it by an additional 30 kWp already this year.
3. How does photovoltaics fit into the whole concept of the energy transition to sustainable sources?
Solar power plants, in addition to being a renewable source, significantly fit into the concept of consumer involvement in the electricity market, which is an essential part of the concept of sustainable development of electricity and human society as a whole. In addition to the regulation of consumption and energy storage, people or businesses can thus participate in the production of electricity, each at a scale that is accessible to them. Such ability to create power plants of various sizes with efficiency, cost and maintenance accessible to both ordinary people and businesses or energy companies is a specific feature of solar generation. The production of energy, for example from coal or biomass, wind and other sources, involves operating costs that make it disadvantageous for small volumes of production, thus limiting its ownership almost exclusively to energy companies and large enterprises, thus excluding households.
4. Are some of your projects from this area already in the phase of real use?
The solar projects of our innovation center often fall under research and thus have a longer path to the market, usually via pilot installations. Of the projects we have been involved in as part of Eaton's global team, this is xStorage Home, which has been available on the European and world market for over four years. It is also a microgrid control system that is being piloted at Eaton facilities and several locations in the United States. We are currently working on the installation of a pilot microgrid connecting classic alternating current and newly direct current systems with advanced self-regulation and resilience properties. As another example of existing projects using solar energy is integration of the Eaton xStorage Home system into the xComfort home automation system. Through the SHC (Smart Home Controller), xComfort users get remote access to data from the battery storage and have the possibility to define basic energy management scenarios, e.g. optimization of domestic water heating depending on the energy production from the solar panels and the current state of the battery storage.
5. What major Eaton-wide PV or energy storage projects can you name?
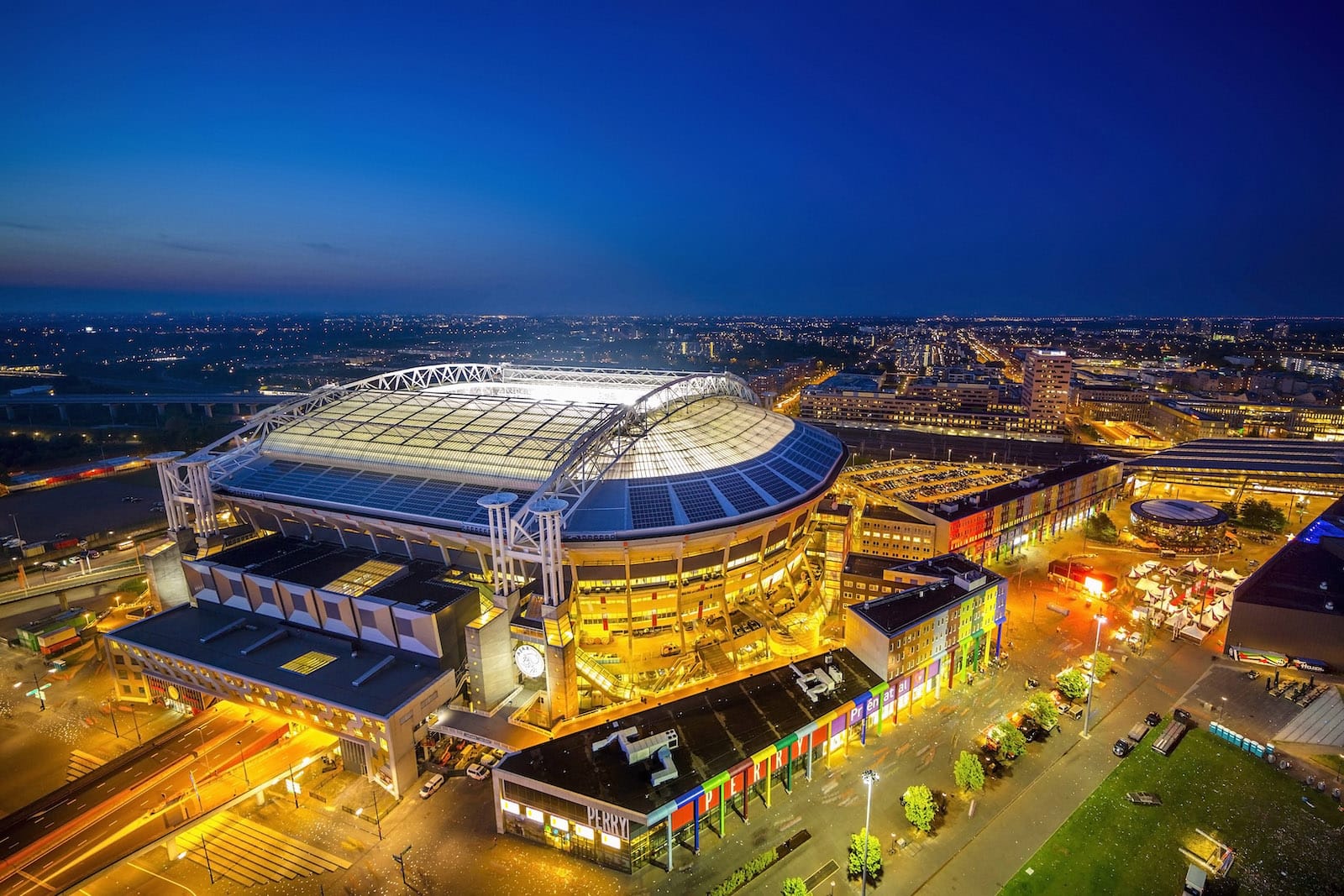
Certainly Johan Cruijff Arena in Amsterdam and energy storage solutions at the football stadium to cover peak demand during sporting events, which also includes the provision of support services for the distribution company in the area of regulating the electricity network outside of event times. Next, I would like to mention the Eaton Wadeville microgrid project in South Africa, in which we provide power generation for our factory in situations of frequent power outages and also reduce the cost of electricity. In line with our 2030 sustainability goals, we recently installed solar panels at our factory in Busag, Romania to reduce the carbon footprint of our manufacturing facility. As part of the internal GreenUp Awards, which provide funding for internal projects in the field of sustainability, our innovation center in Roztoky won funding for the expansion of solar panels, energy storage and chargers for electric cars.









Discussion of the article
Discussion is not open for this article.