Passwords are not 100% secure and there is always a risk of their leakage through a direct attack on your accounts or a large-scale attack on online services that typically store user data on clouds. Therefore, it is also strongly recommended to use password managers and two-factor authentication applications.
With data breaches happening all the time and nefarious entities using them to sell compromised credentials on dark web markets, it doesn't hurt to check if any of your passwords have been stolen. After all, yesterday we also informed you that Samsung itself faced a data leak.
You could be interested in

Using the built-in tool in password managers
Password managers are the best way to keep your online accounts secure for many reasons. They design and store security codes and passwords in encrypted databases, so you don't have to enter them repeatedly, and most importantly, you don't even have to remember them. However, many of these tools also allow you to check the status of your codes and passwords.
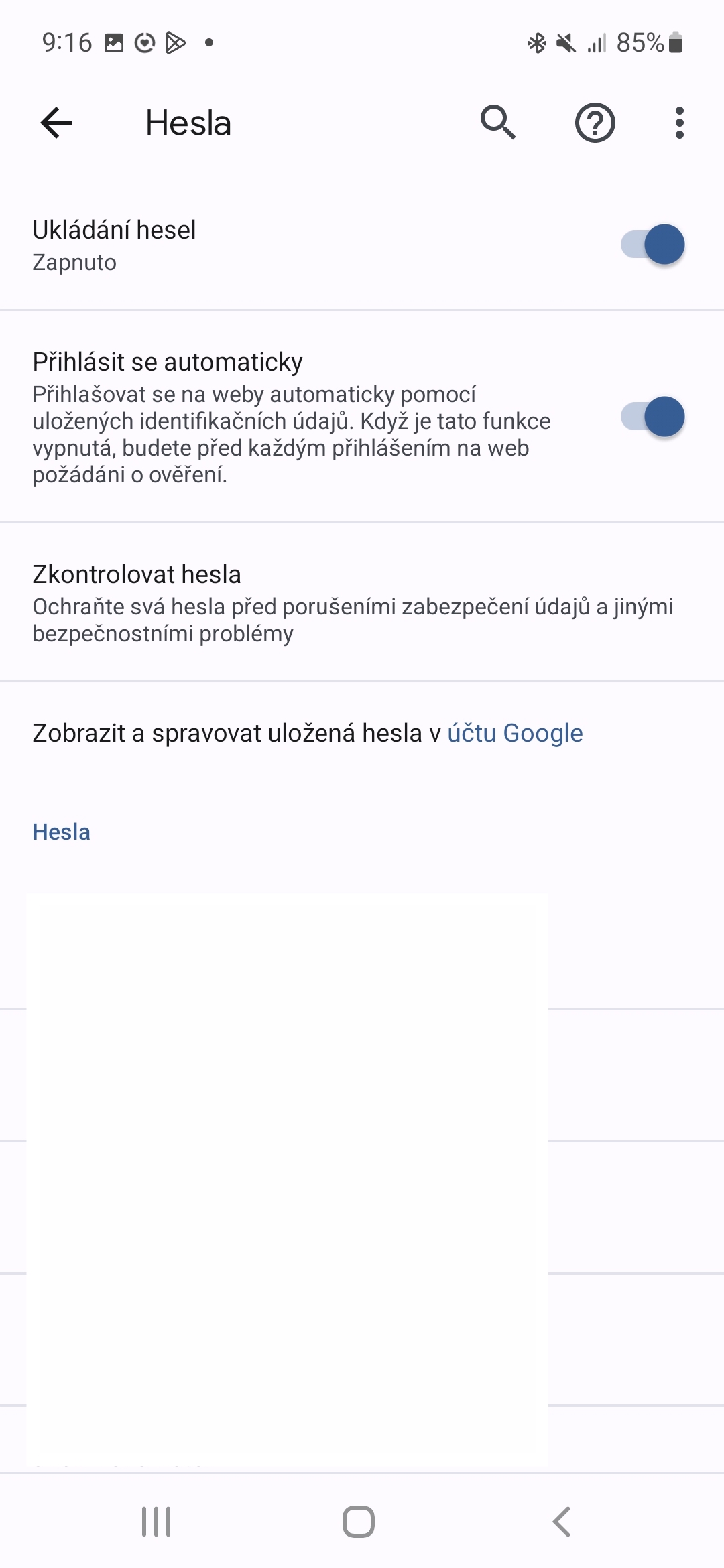
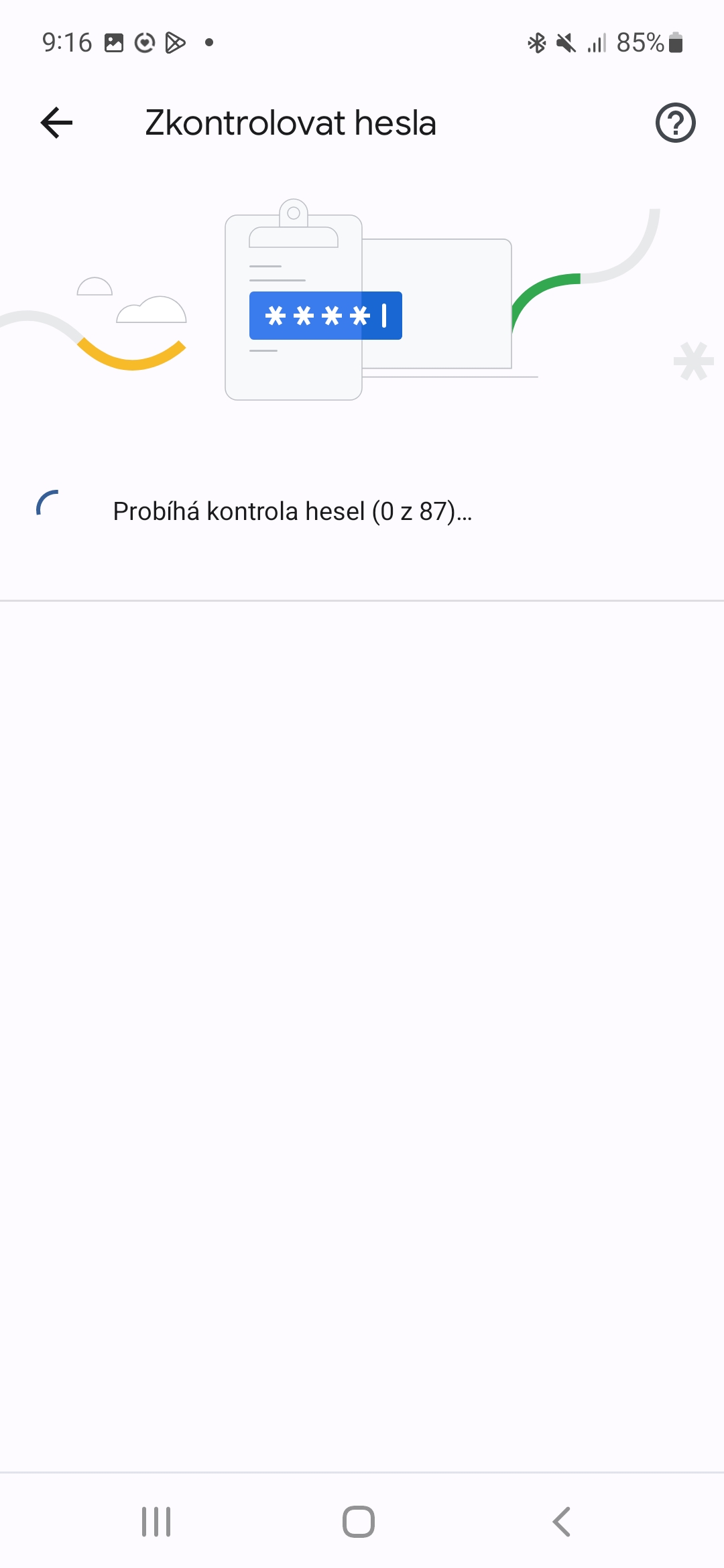
For example, even just the Google password manager in the browser Chrome has a password checker feature that diagnoses problems with them. Go to Settings -> Passwords -> Check Passwords. Another option is service Dashlane, which provides monitoring of the dark web and the status of your credentials.
An important password manager is 1Password, which automatically checks passwords in the background and alerts you to potential breaches. This is thanks to the built-in function Watchtower that works on the Pwned Passwords API. Like Pwned Passwords, it is updated when new security breaches are reported and added to the Have I Been Pwned database. And if any of your passwords are found in such a breach, you're notified immediately.
Have I Been Pwned
This is a trusted site created in 2013 by Troy Hunt, Regional Director and MVP at Microsoft. It is popular in the cyber security world for exposing data security breaches and educating technology professionals. And with details on nearly 11 billion compromised accounts, its tool is the most popular way to find out if your password is still safe.
Using the service is very easy. Just go to official website on your smartphone or computer browser and enter your email address or phone number. Within seconds, you'll get back the details of any breach where your credentials were compromised.
The platform also has several other handy tools to ensure the security of your login information. It is also a tool for checking passwords. The latter allows users to reverse the process described above and allows you to enter a password directly to see if it has been cracked. You can also use the domain lookup service to check the security of all emails associated with their domain name with one click.
The important thing is that this tool is safe. Even in the case of compromised accounts, the relevant passwords are not stored in the database, reducing the risk of further problems. In addition, the implementation of a mathematical property called "k-anonymity" and the backing of Cloudflare means that all the data you enter into the tool is safe from leaks.
You could be interested in
Check your accounts for suspicious activity.
Password managers and related tools help catch account breaches before they escalate. However, most social accounts post regularly informace on activities that can help detect potential breaches. For example, Google will notify you when your password is changed or when an unknown device logs into your account. Always check such emails and take appropriate action if necessary.
Chrome has many security and privacy features. If you use it as your default browser, watch out for pop-ups when entering passwords online. That's because the app can tap into a database of billions of reported breaches and notify you of a compromise as soon as you start logging into a site.
You could be interested in
While the methods described here are fine for checking the security of your passwords, they don't account for all the variables. This is because they rely on existing databases of known and verified breach records. This makes them blind to compromises that have not yet been reported. It follows that it is better to avoid the risk directly, and of course with strong and secure passwords and the use of appropriate administrators.